++ 50 ++ heart anatomy labeled 972025-Heart anatomy labeled diagram
This article lists a series of labeled imaging anatomy cases by system and modality Brain CT head noncontrast axial CT head noncontrast coronal CT head noncontrast sagittal CT head angiogram axial CT head angiogram coronal CT headNormal Anatomy The crista terminalis is now just visible and will be readily visualized on views that follow The crista terminalis is a vertical fibromuscular ridge that separates the smooth portion of the right atrium, which receives the superior and inferior vena cavae and coronary sinus, from the right atrial appendage and the remainder of the right atrium containing pectinate musclesDetailed anatomical description of the heart valves, including simple definitions and a labeled, fullcolor illustration Anatomy and Function of the Heart Valves Skip to topic navigation

External Anterior Heart Labeling
Heart anatomy labeled diagram
Heart anatomy labeled diagram-EnchantedLearningcom Heart Anatomy Glossary Human Anatomy The heart is a fistsized, muscular organ that pumps blood through the body Oxygenpoor blood enters the right atrium of the heart (via veins called the inferior vena cava and the superior vena cava) The blood is then pumped into the right ventricle and thenThe heart is about the size of a closed fist, weighs about 105 ounces and is somewhat coneshaped It is covered by a sack termed the pericardium or pericardial sack The normal heart anatomy consists of a fourchambered, hollow organ It is divided into the left and right side by a muscular wall called the septum



Hand Drawn Illustration Of Human Heart Anatomy Educational Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image
Heart Anatomy Your heart is located between your lungs in the middle of your chest, behind and slightly to the left of your breastbone (sternum) A doublelayered membrane called the pericardium surrounds your heart like a sac The outer layer of the pericardium surrounds the roots of your heart's major blood vessels and is attached byThe left ventricle is the major pumping chamber on the lower left side of the heart that ejects blood into the systemic circuit via the aorta and receives blood from the left atrium;The human heart is a finelytuned instrument that serves the whole body It is a muscular organ around the size of a closed fist, and it sits in the chest, slightly to the left of center
Coronary circulation is the circulation of blood in the blood vessels that supply the heart muscle (myocardium) Coronary arteries supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscle, and cardiac veins drain away the blood once it has been deoxygenated Because the rest of the body, and most especially the brain, needs a steady supply of oxygenated blood that is free of all but the slightestFrom the quiz author Ummmmmmm it's pretty self explanatory you label the heart Just remember one thing you're looking at the heart like it's in someone else so right and left are switched around This quiz has tagsHeart Chambers Ventricles – The bottom two heart chambers Atra – The upper two heart chambers Wall Of The Heart Sinoatrial Node – A collection of tissue that releases electrical impulses and defines the rate of contraction for the heart Atrioventricular Bundle – The fibers which transmit cardiac impulses
Heart viewed from above, atria removed, base of ventricles exposed Left coronary artery visible at left Heart viewed from the front Coronary arteries (labeled in red text) and other major landmarks (in blue text) Left coronary artery is at upper right in the image Anatomy figure 0301 at Human Anatomy Online,Heart Anatomy (External) Anterior Heart Posterior Heart Heart Chambers The heart must generate enough force that it creates more pressure within the ventricle so that blood can move forward to areas of lower pressure (ie, this is the afterload or resistance to forward flow)EnchantedLearningcom Heart Anatomy Glossary Human Anatomy The heart is a fistsized, muscular organ that pumps blood through the body Oxygenpoor blood enters the right atrium of the heart (via veins called the inferior vena cava and the superior vena cava) The blood is then pumped into the right ventricle and then


Human Heart Anatomy System Human Body Anatomy Diagram And Chart Images
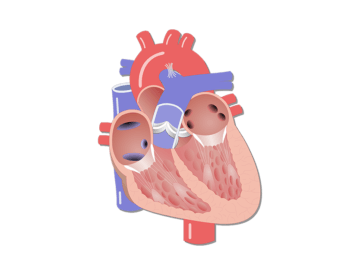


Heart Anatomy
Image heart anatomy – posterior surface view Attached to each AV valve flap are collagen chords called chordae tedineae , which anchor the cusps to the papillary muscles When the heart is completely relaxed, the AV valves flaps hang limp and blood flows into the atria and then through the open AV valve flaps into the ventriclesCorrectly label the following external anatomy of the posterior heart Correctly label the following internal anatomy of the heart Correctly label the following internal anatomy of the heart Correctly sequence the pathway of blood flow through the heart, beginning with the venae cavaeDetailed anatomical description of the heart valves, including simple definitions and a labeled, fullcolor illustration Anatomy and Function of the Heart Valves Skip to topic navigation
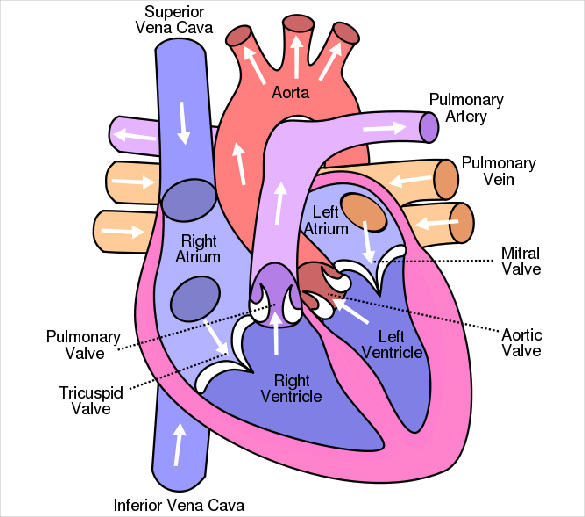


Heart Diagram 15 Free Printable Word Excel Eps Psd Template Download Free Premium Templates



Anatomy Of The Heart A Cross Section Of The Heart Wall Showing The Download Scientific Diagram
Detailed anatomical description of the heart valves, including simple definitions and a labeled, fullcolor illustration Anatomy and Function of the Heart Valves Skip to topic navigationThe heart is the organ that helps supply blood and oxygen to all parts of the body Heart anatomy focuses on the structure and function of the heartHeart Anatomy Your heart is located between your lungs in the middle of your chest, behind and slightly to the left of your breastbone (sternum) A doublelayered membrane called the pericardium surrounds your heart like a sac The outer layer of the pericardium surrounds the roots of your heart's major blood vessels and is attached by
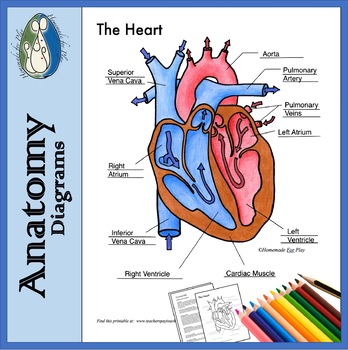


Heart Diagrams For Labeling And Coloring With Reference Chart And Summary



Heart Cross Section Labeled Canvas Print Barewalls Posters Prints Bwc
The circulatory system Locate the arteries and veins of the circulatory system The internal organs Identify the internal organs The heart an image of the heart with blank labels attached The circulatory system upper body image, with blank labels attachedThe anatomy of the heart was made easy in a previous EZmed video and post, where we learned tricks to remember the main cardiac structures shown below Check out the anatomy of the heart linked below, as that will be a great review of the main cardiac structures before learning the blood flow!Coloring with labeled anatomy, Heart dissection lab, Your guide to dissection, Lab chicken heart dissection Heart Dissection Worksheets Learny Kids Sheep heart dissection Lab Anatomy & Physiology Purpose of this lab To review the structural characteristics of the human heart and to examine the major features of a mammalian heart



Human Heart With Labels On White Background Stock Photo Download Image Now Istock



Anatomy Of The Heart Human Heart Anatomy Human Anatomy And Physiology Heart Anatomy
Heart Anatomy Label Me!In addition to the anatomy of the heart more add to cart 3B Smart Anatomy 5 year warranty Classic Human Heart Model, 2 part 3B Smart Anatomy $ 7300 Item G08 Highly detailed 2part human heart model at a price you will love The front heart wall is detachable to reveal the chambers and valves inside the human heartHeart blood flow heart flow learn biology heart anatomy cardiac nursing anatomy study circulatory system anatomy and physiology study human body Its function is to pump blood to the lungs and around the body So what i want to do first is to label the different structures in our heart so 14 Human Heart Blood Flow Diagram Right and left
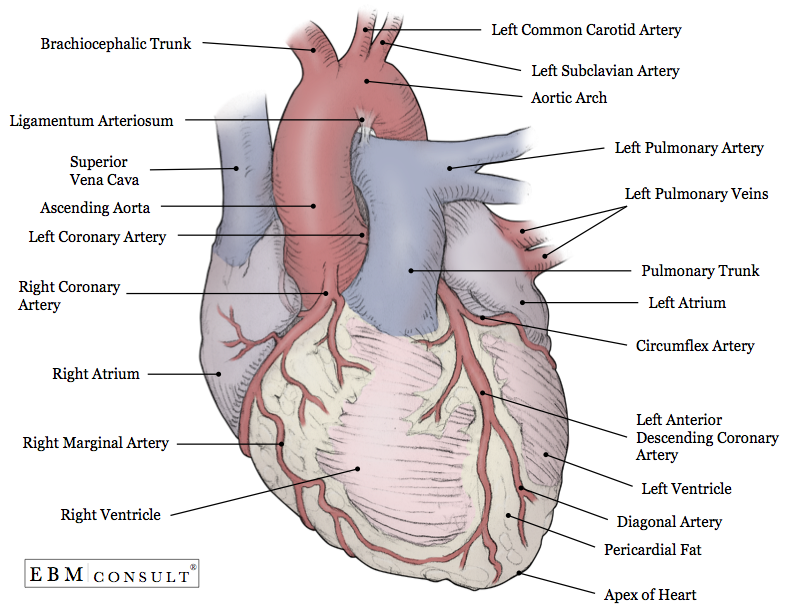


Anatomy Heart External



Diagram A Well Labelled Diagram Of Inside The Human Heart Full Version Hd Quality Human Heart Diagrampart Dsimola It
The heart is a mostly hollow, muscular organ composed of cardiac muscles and connective tissue that acts as a pump to distribute blood throughout the body's tissuesBecause the heart points to the left, about 2/3 of the heart's mass is found on the left side of the body and the other 1/3 is on the right Anatomy of the Heart Pericardium The heart sits within a fluidfilled cavity called the pericardial cavity The walls and lining of the pericardial cavity are a special membrane known as the pericardiumGross anatomy The heart has a somewhat conical form and is enclosed by the pericardium It is positioned posteriorly to the body of the sternum with onethird situated on the right and twothirds on the left of the midline Its leftsided orientation is formally known as levocardia (cf dextrocardia)



External Anterior Heart Labeling


Heart Anatomy Anatomy And Physiology
Anatomy and Function of the Coronary Arteries Facebook Twitter Linkedin Print This can lead to a heart attack and possibly death Atherosclerosis (a buildup of plaque in the inner lining of an artery causing it to narrow or become blocked) is the most common cause of heart diseaseThe human heart is a finelytuned instrument that serves the whole body It is a muscular organ around the size of a closed fist, and it sits in the chest, slightly to the left of centerYour heart is an amazing organ It continuously pumps oxygen and nutrientrich blood throughout your body to sustain life This fistsized powerhouse beats (expands and contracts) 100,000 times



Heart Illustrated Anatomy


Heart Models
Pictureofheartlabeled Diagram Chart Human body anatomy diagrams and charts with labels This diagram depicts Picture Of Heart LabeledHuman anatomy diagrams show internal organs, cells, systems, conditions, symptoms and sickness information and/or tips for healthy livingHeart Anatomy Label Me!The right ventricle is the major pumping chamber on the lower right side of the heart that ejects blood into the pulmonary circuit via the pulmonary trunk and receives blood from the right atrium



Heart Anatomy Vector Illustration Labeled Organ Structure Educational Scheme Stock Illustration Download Image Now Istock
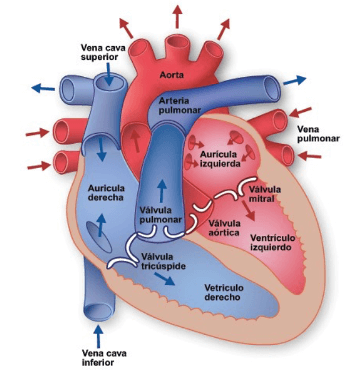


The Heart Medical Spanish
Heart Anatomy Your heart is located between your lungs in the middle of your chest, behind and slightly to the left of your breastbone (sternum) A doublelayered membrane called the pericardium surrounds your heart like a sac The outer layer of the pericardium surrounds the roots of your heart's major blood vessels and is attached byHeart blood flow heart flow learn biology heart anatomy cardiac nursing anatomy study circulatory system anatomy and physiology study human body Its function is to pump blood to the lungs and around the body So what i want to do first is to label the different structures in our heart so 14 Human Heart Blood Flow Diagram Right and leftVentricle one of the primary pumping chambers of the heart located in the lower portion of the heart;



Labeled Heart Diagrams Bryon Spicci S Web Page



Hand Drawn Illustration Of Human Heart Anatomy Educational Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image
Label the heart In this interactive, you can label parts of the human heart Drag and drop the text labels onto the boxes next to the diagram Selecting or hovering over a box will highlight each area in the diagram Pulmonary vein Carries oxygenated blood from the lungs Pulmonary veinThe heart is a mostly hollow, muscular organ composed of cardiac muscles and connective tissue that acts as a pump to distribute blood throughout the body's tissuesHeart Anatomy Heart Wall Epicardium The outer layer of the wall of the heart Myocardium The muscular middle layer of the wall of Cardiac Conduction Cardiac conduction is the rate at which the heart conducts electrical impulses Heart nodes and Cardiac Cycle The Cardiac cycle is the



Heart Anatomy Mydr Com Au



Chapter Cardiovascular System Flashcards Quizlet
Introduction to Anatomy of the Heart This course is designed to give you a comprehensive introduction to the anatomy of the heart It is an interactive, lecture based course covering the underlying concepts and principles related to human gross anatomy of the heart and related structuresAnatomy of the human heart and coronaries how to visualize anatomic structures This tool provides access to several medical illustrations, allowing the user to interactively discover heart anatomy Images are labelled, providing an invaluable medical and anatomical tool The test mode allows instant evaluation of user progressHeart Anatomy (External) Anterior Heart Posterior Heart Heart Chambers The heart must generate enough force that it creates more pressure within the ventricle so that blood can move forward to areas of lower pressure (ie, this is the afterload or resistance to forward flow)



Hand Drawn Illustration Human Heart Anatomy Stock Vector Royalty Free



Heart Anatomy Anatomy And Physiology
Heart Anatomy Labeled Diagram, Structures2X Enlarged Human Heart Anatomical Model,Anatomically Accurate Heart Model Human Skeleton Anatomy for Science Classroom Study Display Teaching Medical Model 45 out of 5 stars 29 $59 $ 58 99 ($1475/Item) 5% coupon applied at checkout Save 5% with coupon Get it as soon as Fri, Mar 12Heart Anatomy Labeled Diagram, Structures



Heart Cross Sectional View Shawna R Snyder Illustration


3
The heart is a muscular organ about the size of a fist, located just behind and slightly left of the breastbone The heart pumps blood through the network of arteries and veins called theLabeledheart Diagram Chart Human body anatomy diagrams and charts with labels This diagram depicts Labeled Heart Human anatomy diagrams show internal organs, cells, systems, conditions, symptoms and sickness information and/or tips for healthy livingHeart anatomy The heart has five surfaces base (posterior), diaphragmatic (inferior), sternocostal (anterior), and left and right pulmonary surfaces It also has several margins right, left, superior, and inferior The right margin is the small section of the right atrium that extends between the superior and inferior vena cava


Label The Heart Science Learning Hub


Q Tbn And9gcr Tz1njqe8ssrfjfyqlj9jjcr Ufmnfukbilaehxpdwujznr2 Usqp Cau
The heart is about the size of a closed fist, weighs about 105 ounces and is somewhat coneshaped It is covered by a sack termed the pericardium or pericardial sack The normal heart anatomy consists of a fourchambered, hollow organ It is divided into the left and right side by a muscular wall called the septumInstructions for Human heart anatomy The heart is a fourchambered muscular organ which, through a twopart contraction, pumps oxygen and nutrient rich blood around the body and consists of many important parts to make this work Learn all the parts in this heart labeling game The 13 heart terms practiced in this game areThe anatomy of the heart was made easy in a previous EZmed video and post, where we learned tricks to remember the main cardiac structures shown below Check out the anatomy of the heart linked below, as that will be a great review of the main cardiac structures before learning the blood flow!
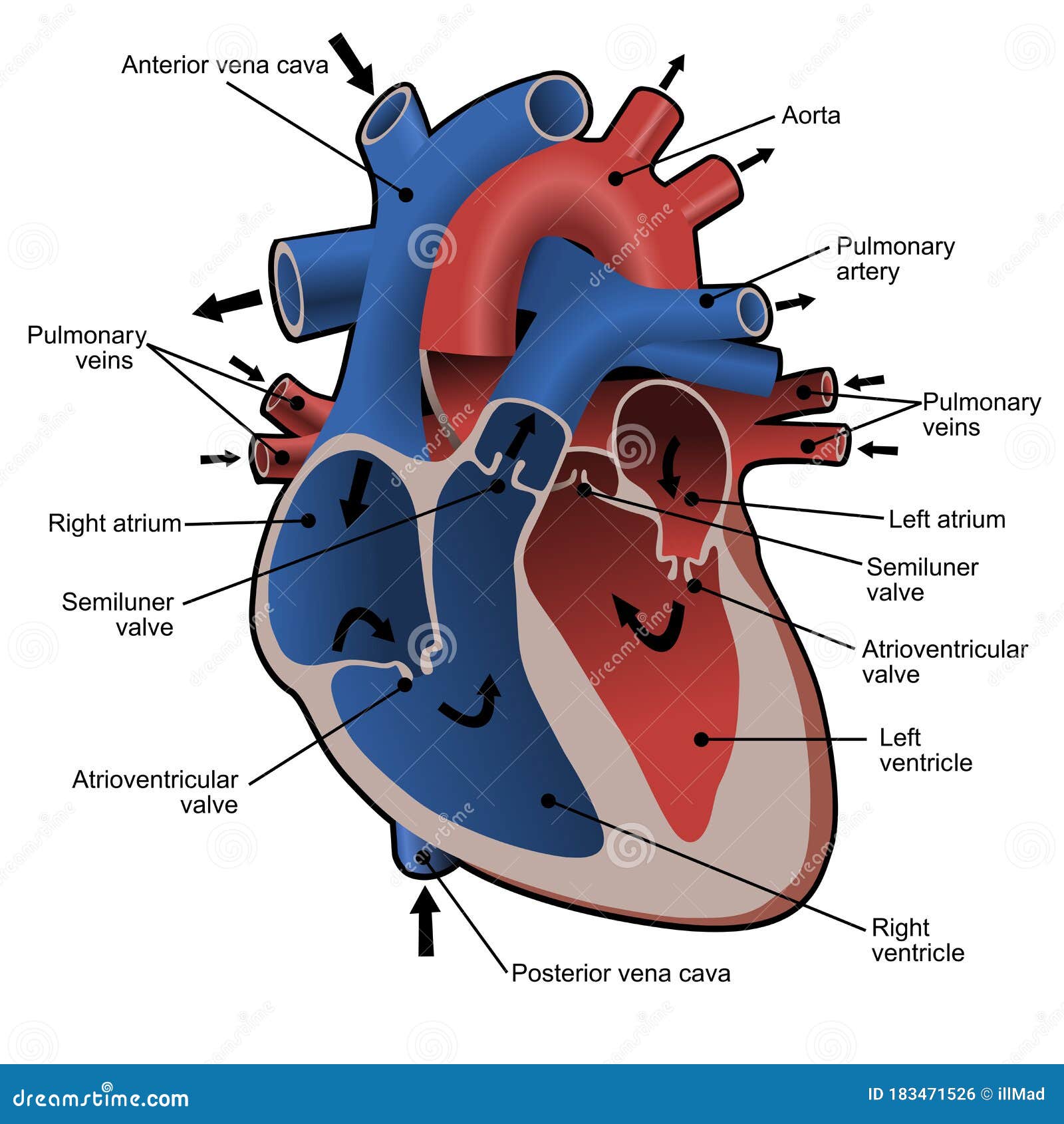


Heart Labeled Stock Illustrations 174 Heart Labeled Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime
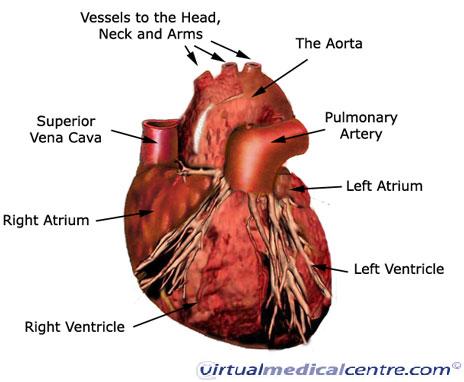


Cardiovascular System Heart Anatomy Healthengine Blog
Labeledheart Diagram Chart Human body anatomy diagrams and charts with labels This diagram depicts Labeled HeartHuman anatomy diagrams show internal organs, cells, systems, conditions, symptoms and sickness information and/or tips for healthy livingHeart blood flow heart flow learn biology heart anatomy cardiac nursing anatomy study circulatory system anatomy and physiology study human body Its function is to pump blood to the lungs and around the body So what i want to do first is to label the different structures in our heart so 14 Human Heart Blood Flow Diagram Right and leftLabeled heart diagrams Take a look at our labeled heart diagrams (see below) to get an overview of all of the parts of the heart Once you're feeling confident, you can test yourself using the unlabeled diagrams of the parts of the heart below
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-598167278-5b47abf4c9e77c0037f4fedf.jpg)


The Anatomy Of The Heart Its Structures And Functions
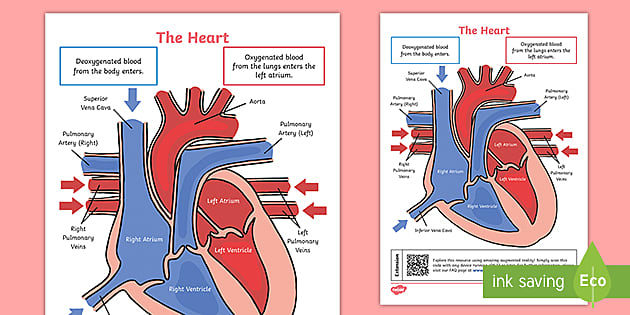


Ks2 Heart Diagram Qr Labelling Activity Science Twinkl
Coronary circulation is the circulation of blood in the blood vessels that supply the heart muscle (myocardium) Coronary arteries supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscle, and cardiac veins drain away the blood once it has been deoxygenated Because the rest of the body, and most especially the brain, needs a steady supply of oxygenated blood that is free of all but the slightest



Chordae Tendineae Wikipedia
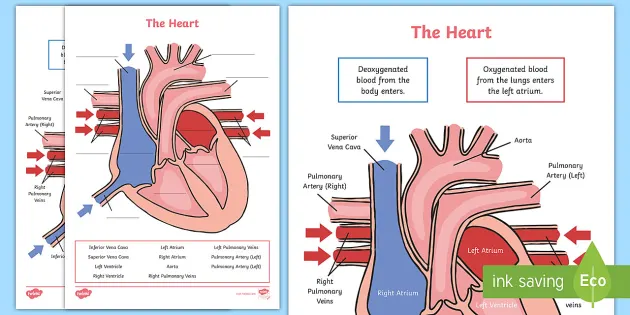


Simple Heart Diagram Labeling Activity Teacher Made



19 1 Heart Anatomy Anatomy Physiology



Heart Cross Section Labeled Cross Section Of Human Heart Eps8 Canstock
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/10912/labeled_heart_diagram.png)


Diagrams Quizzes And Worksheets Of The Heart Kenhub
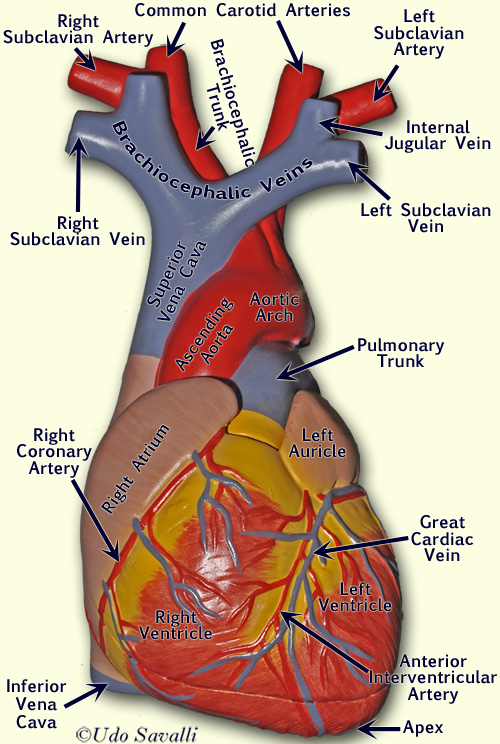


Bio2 Heart Model
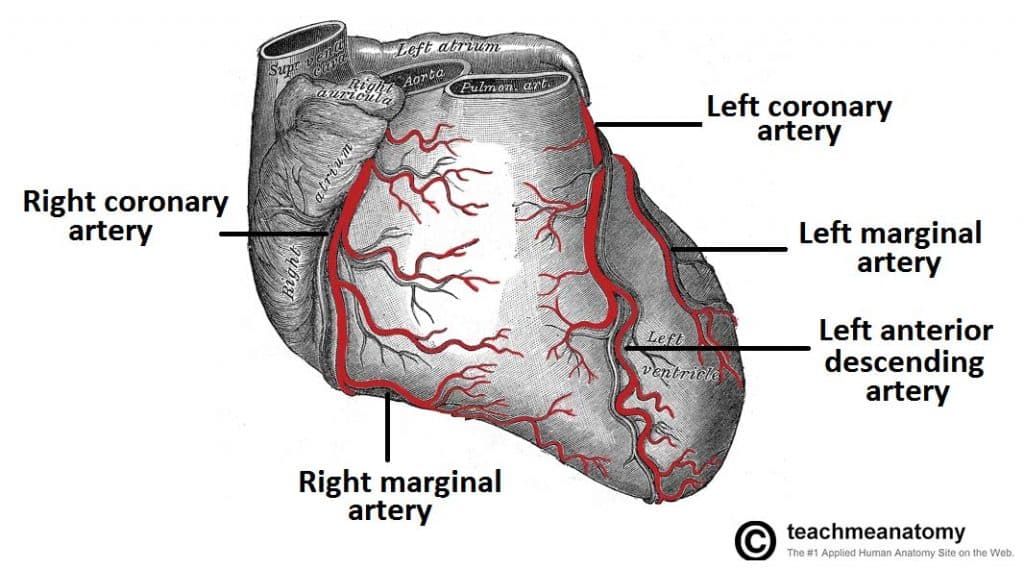


Vasculature Of The Heart Teachmeanatomy
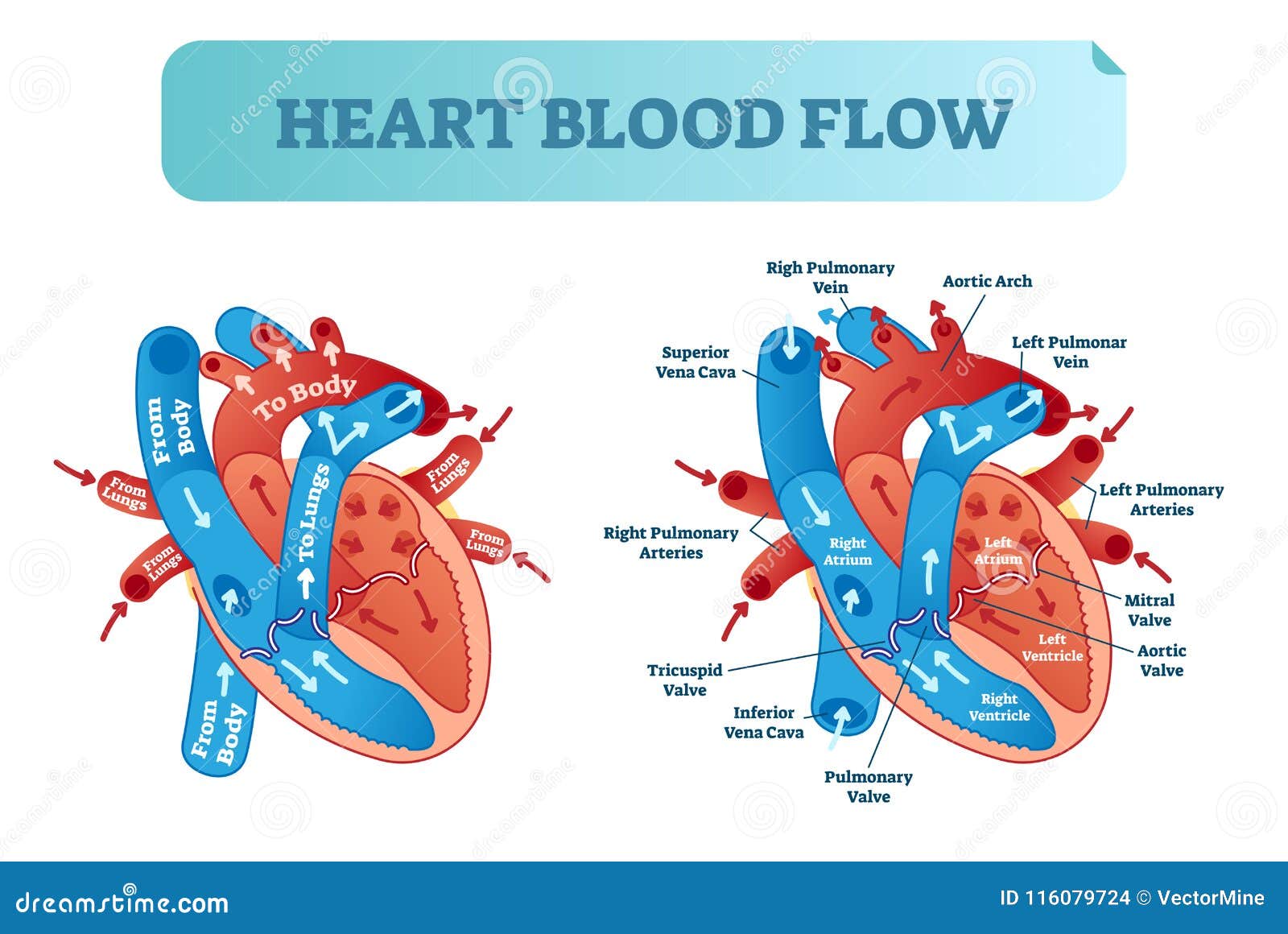


Heart Blood Flow Circulation Anatomical Diagram With Atrium And Ventricle System Vector Illustration Labeled Medical Poster Stock Vector Illustration Of Cardiac Coronary


Cardiac Anatomy And Physiology Revision Www Forensicmed Co Uk



Free Printable Heart Diagram For Kids Labeled And Unlabeled



Heart Valve Anatomy Britannica
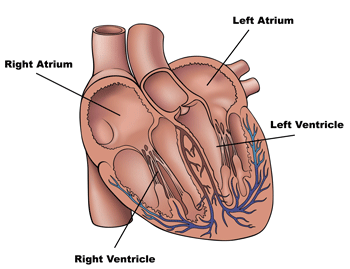


Human Heart Diagram Side View And Top View
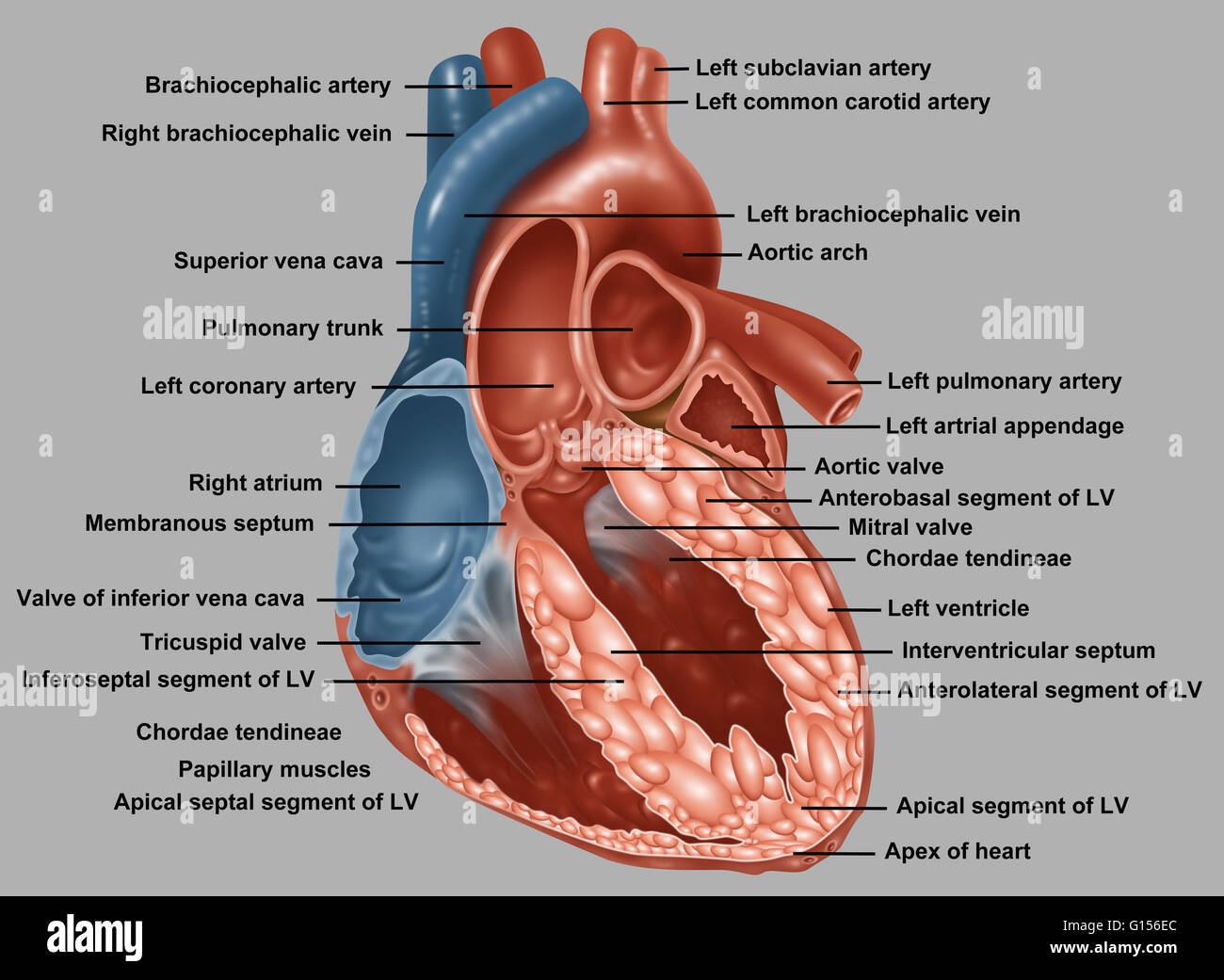


Anatomy Of A Normal Human Heart With Everything Labeled Stock Photo Alamy
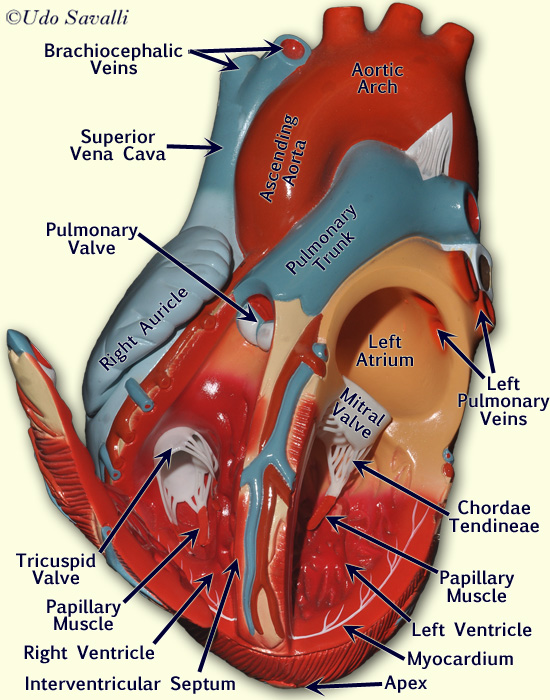


Bio2 Heart Model



Lesson The Heart External Structure Encounter Edu


Coronary Circulation Wikipedia



Science Source Stock Photos Video Heart Anatomy Labeled Illustration


Q Tbn And9gcscoec9ikb2odtoh Amsskzy0epgx Ak9b76dloef4is7mzvdb4 Usqp Cau



Vector Art Human Heart Muscle Structure Anatomy Diagram Clipart Drawing Gg Gograph


Heart Diagrams For Friday S Quiz December 9th Anatomy Phys 3 A B Powers S1


Free Heart Diagram Unlabeled Download Free Clip Art Free Clip Art On Clipart Library


Heart Anatomy Using Models



Science Source Stock Photos Video Heart Interior Labeled Illustration



Hand Drawn Illustration Of Human Heart Anatomy Educational Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image


Heart Models



How The Heart Works Diagram Anatomy Blood Flow



Anatomy Of The Human Heart Internal Structures



Anatomy Of The Heart Emt Training Station


3


Label Heart Anatomy Diagram Printout Enchantedlearning Com
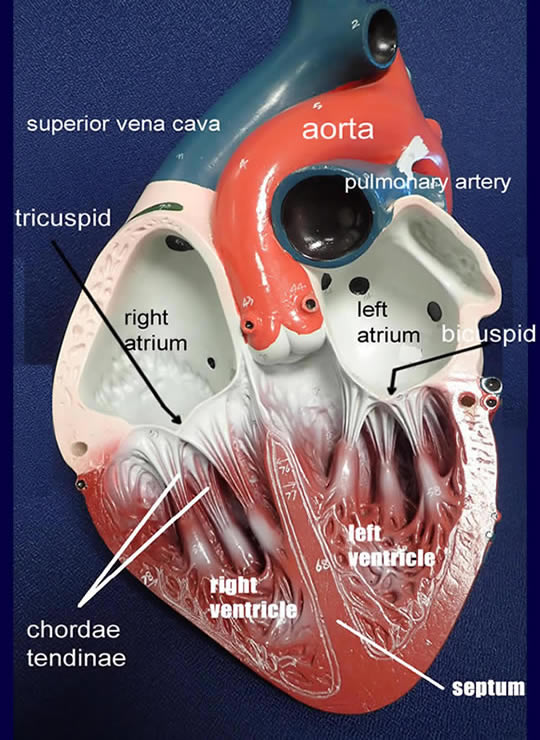


Heart Models
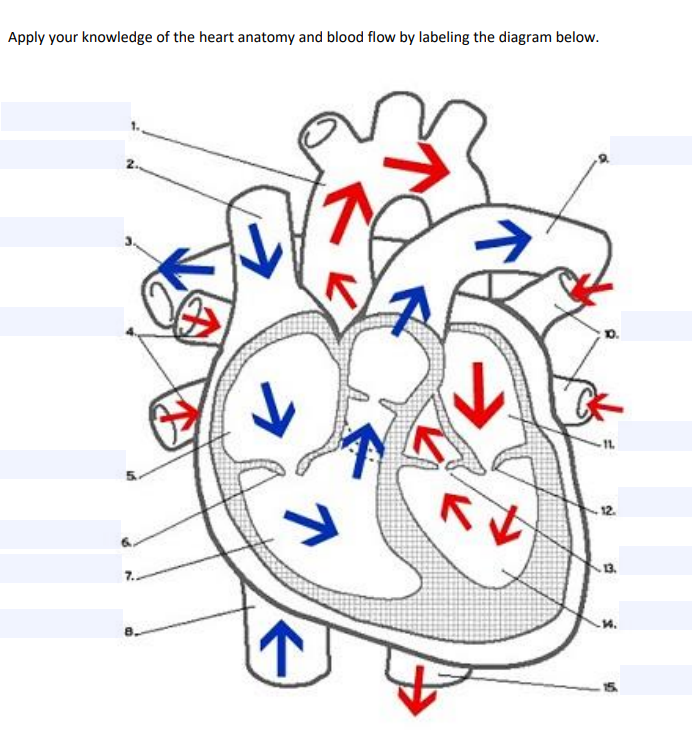


Solved Apply Your Knowledge Of The Heart Anatomy And Bloo Chegg Com


Heart Anatomy Glossary Printout Enchantedlearning Com



Heart Labeling Flashcards Quizlet


Heart Models



19 Human Heart Labeled Illustrations Clip Art Istock



Heart Cross Section Labelled Medical Stock Images Company



Heart Anatomy Heart Dissections Heart Labeling Mirandasanatomy Physiologyblog
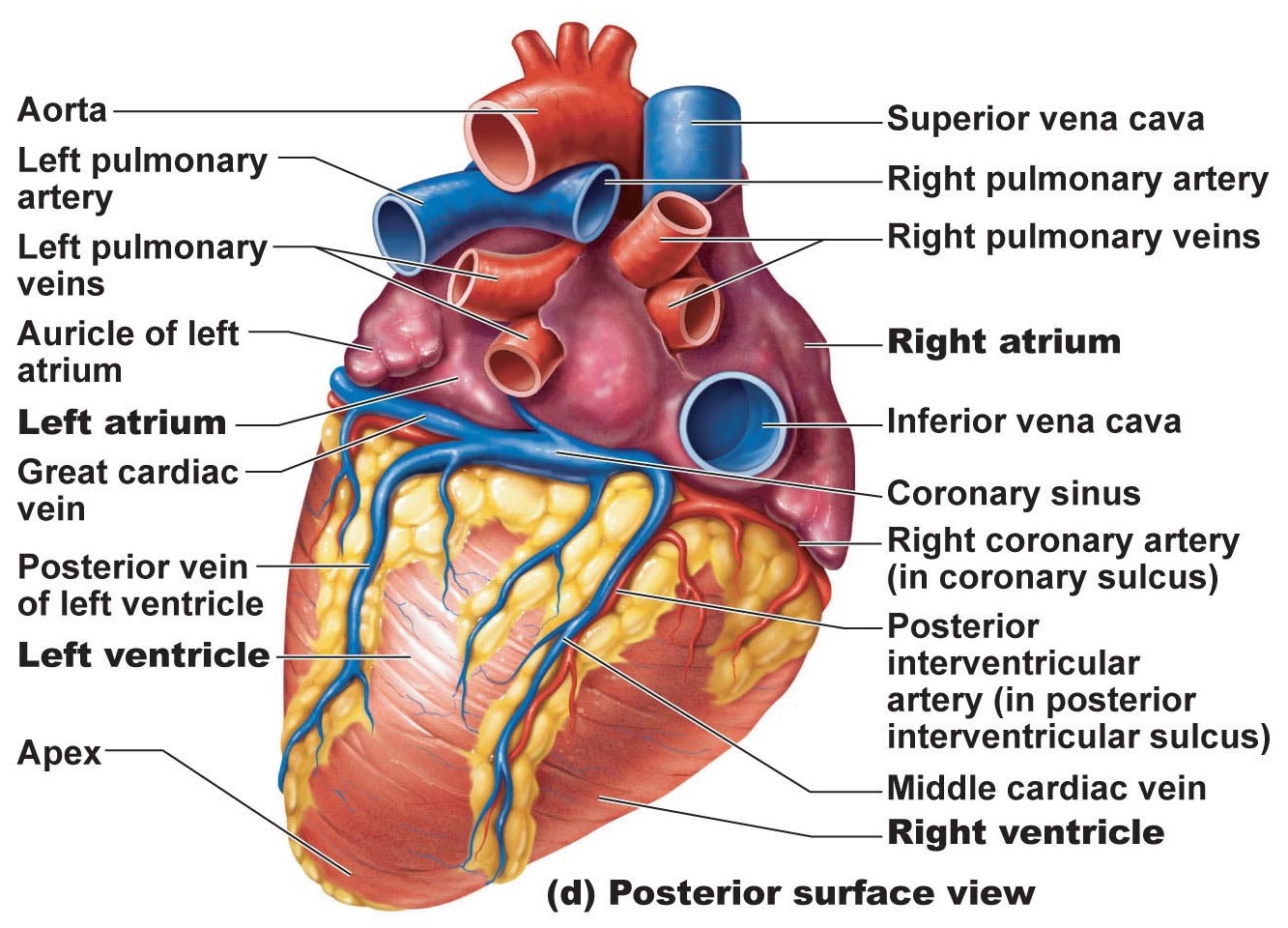


Heart Anatomy Chambers Valves And Vessels Anatomy Physiology



Labeling Heart Diagram Human Anatomy



Anatomy Human Heart Cross Sectional Diagram Stock Vector Royalty Free



Labeled Anterior Heart Anatomy Page 1 Line 17qq Com


Anatomy Of The Heart


Cardiovascular System Of The Dog



A P Anatomy Physiology The Unity Of Form And Function Chapter 19 The Heart Megakit Diagram Quizlet
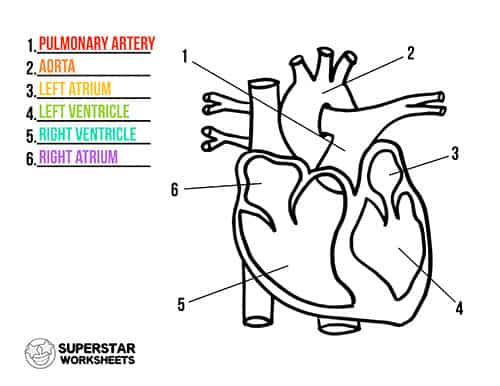


Heart Worksheets Superstar Worksheets



Chapter 27 Heart Anatomy Bio 140 Human Biology I Textbook Libguides At Hostos Community College Library
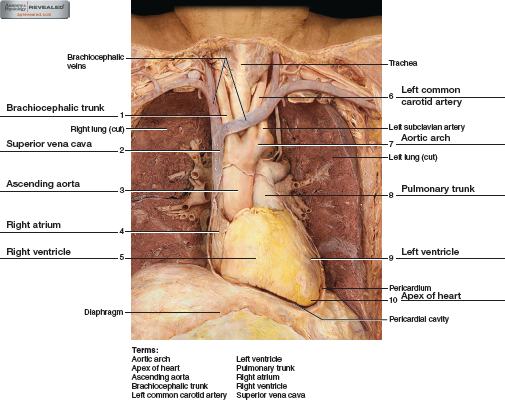


Chapter 44 Solutions Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy Physiology 2nd Edition Chegg Com



Anatomy And Physiology Of The Heart Normal Function Of The Heart Cardiology Teaching Package Practice Learning Division Of Nursing The University Of Nottingham



Labeled Human Heart Koibana Info Anatomy And Physiology Human Heart Anatomy Human Anatomy And Physiology


Heart Dissection Photos



Label The Heart



Human Heart Diagram Labeled Science Trends



Heart Anatomy Yourheartvalve



The Heart 7th Grade Circulatory System


Label The Heart Diagram Human Anatomy
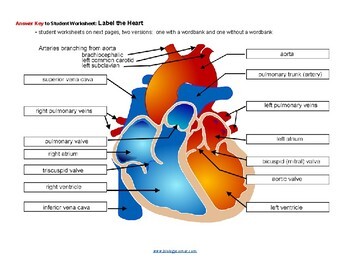


Label The Heart Key By Biologycorner Teachers Pay Teachers


Anterior Human Heart Anatomy Labeled Wall Decal Wallmonkeys Com



Human Heart By Russell Kightley Media



Heart Anatomy Labeled Diagram Structures Blood Flow Function Of Cardiac System Ezmed



Pictures With Parts Labeled Google Search Heart Diagram Human Heart Anatomy Human Heart Diagram



Human Heart Anatomy Heart Anatomy Human Heart Diagram Human Heart Anatomy
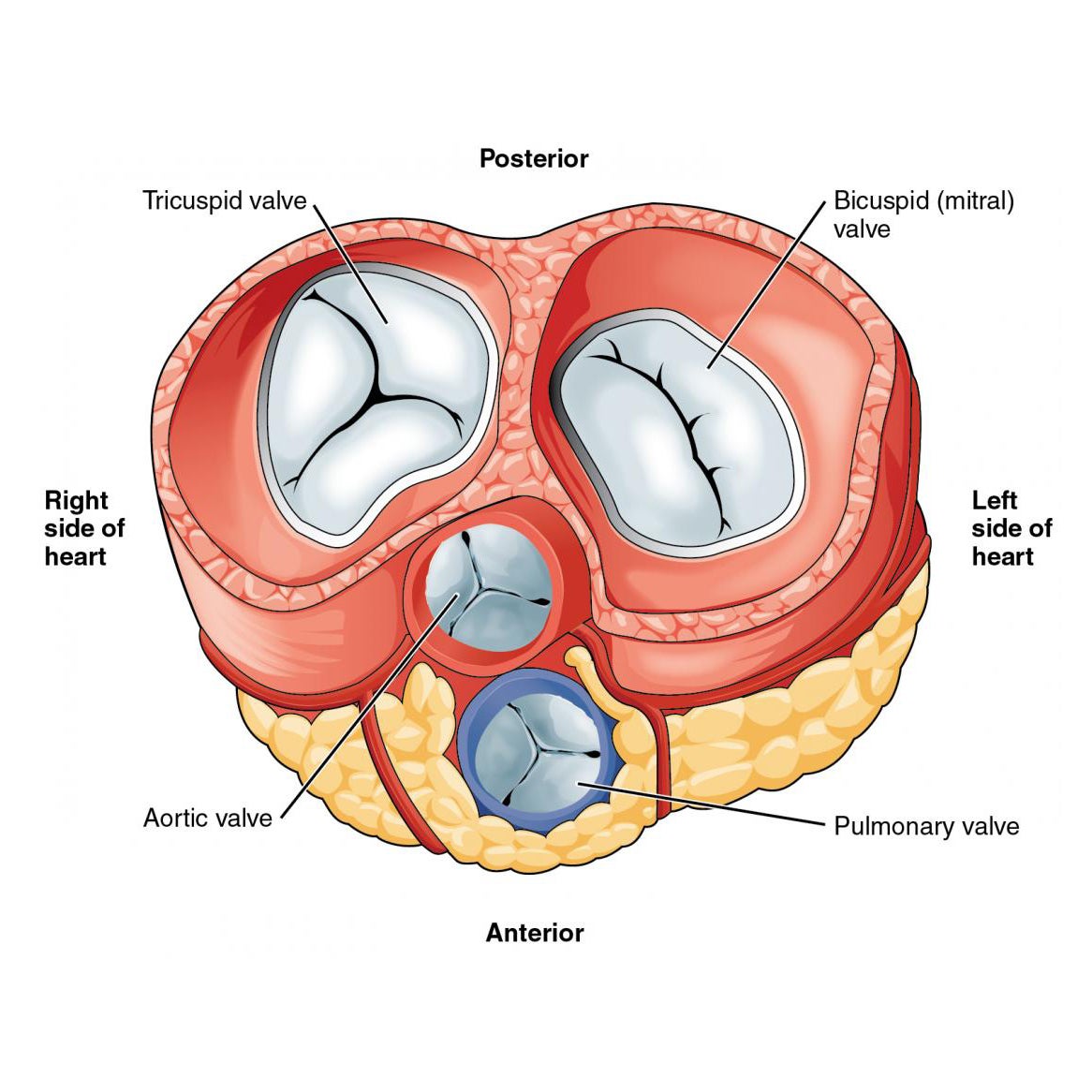


The Heart Anatomy How It Works And More
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11110/Heart_Thumbnail.png)


Heart Anatomy Structure Valves Coronary Vessels Kenhub



31 Critical Thinking Questions
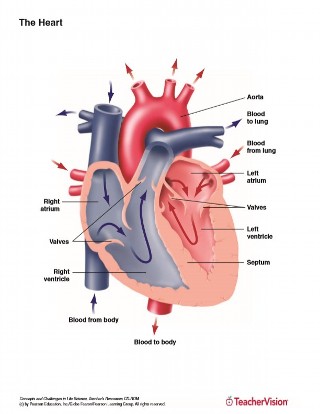


Anatomy Of The Human Heart Printable 6th 12th Grade Teachervision
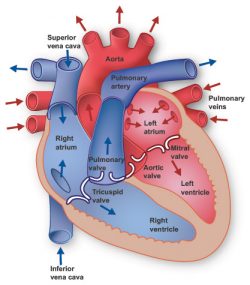


Heart Information Center Heart Anatomy Texas Heart Institute
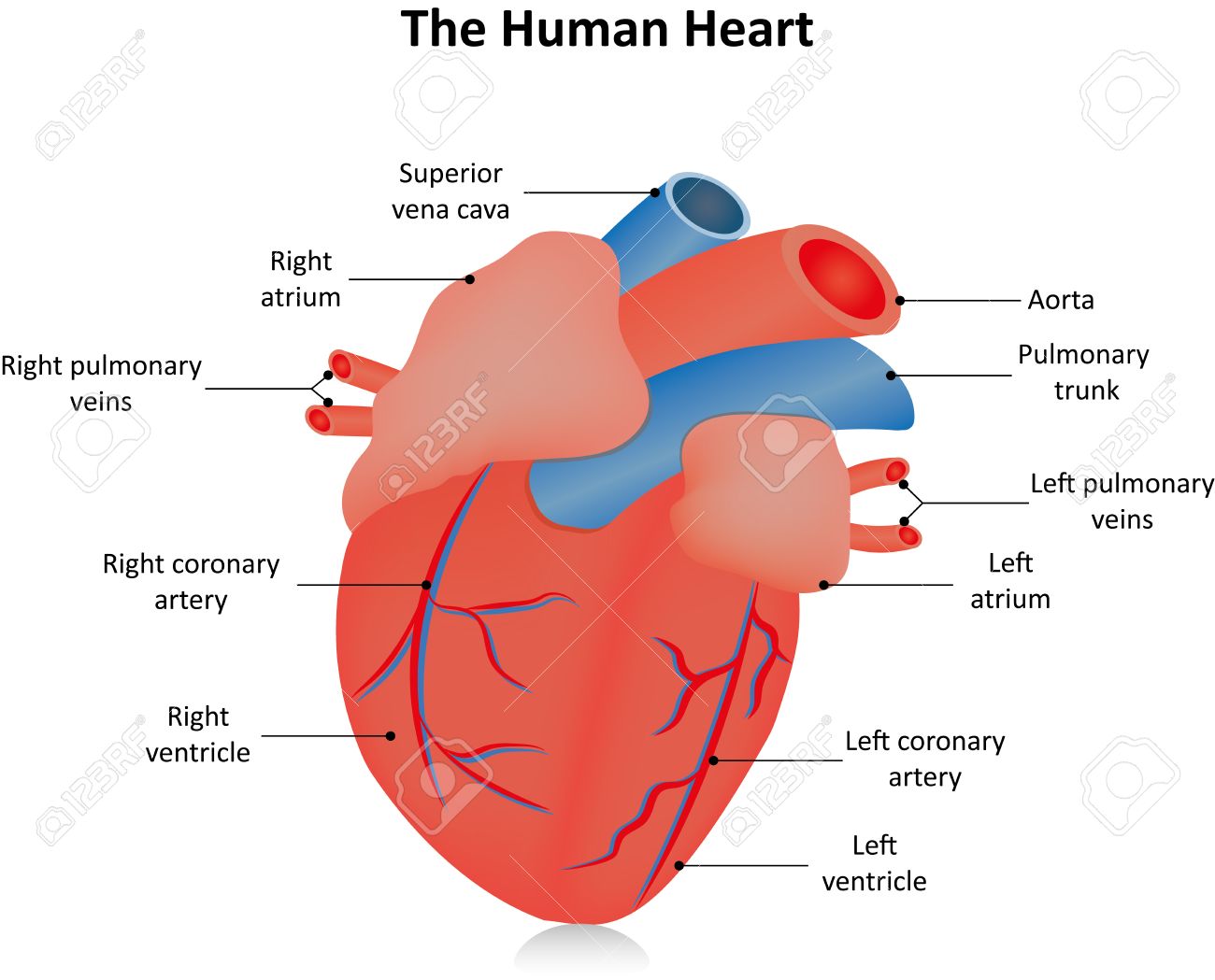


Heart Anatomy Labeled Anatomy Drawing Diagram
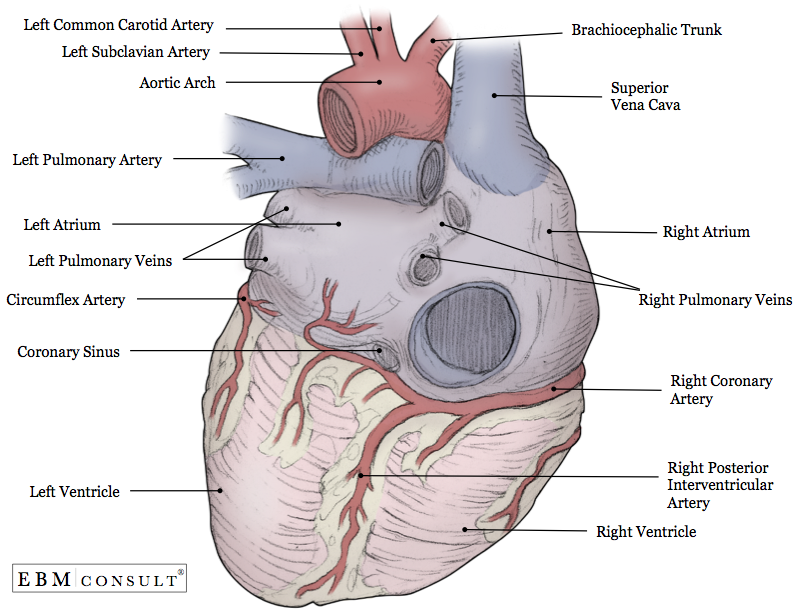


Anatomy Heart External
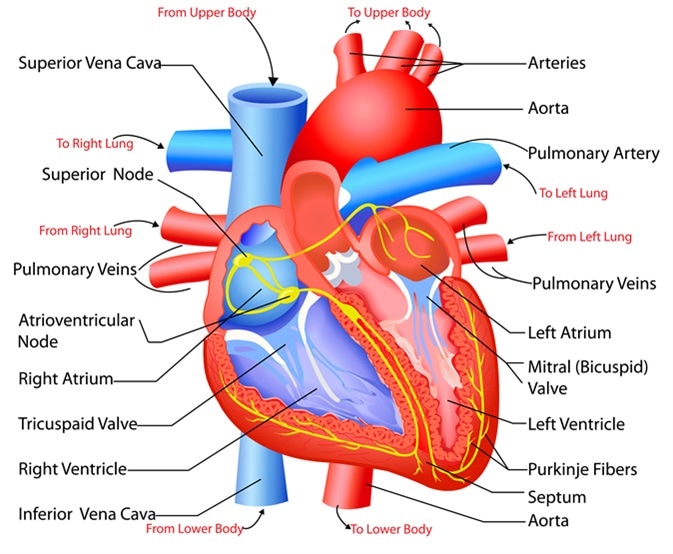


Structure And Function Of The Heart
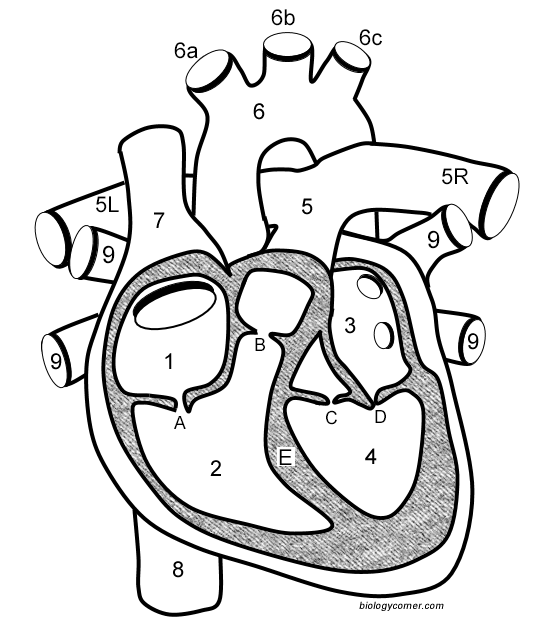


Learn The Anatomy Of The Heart



Pin On Photography



Human Heart Labeled Diagram The Human Heart Diagram Labeled Human Anatomy Photo Human Heart Labeled Diagra Heart Diagram Human Heart Diagram Heart Structure



Heart Anatomy Anatomy And Physiology


コメント
コメントを投稿